Table of content

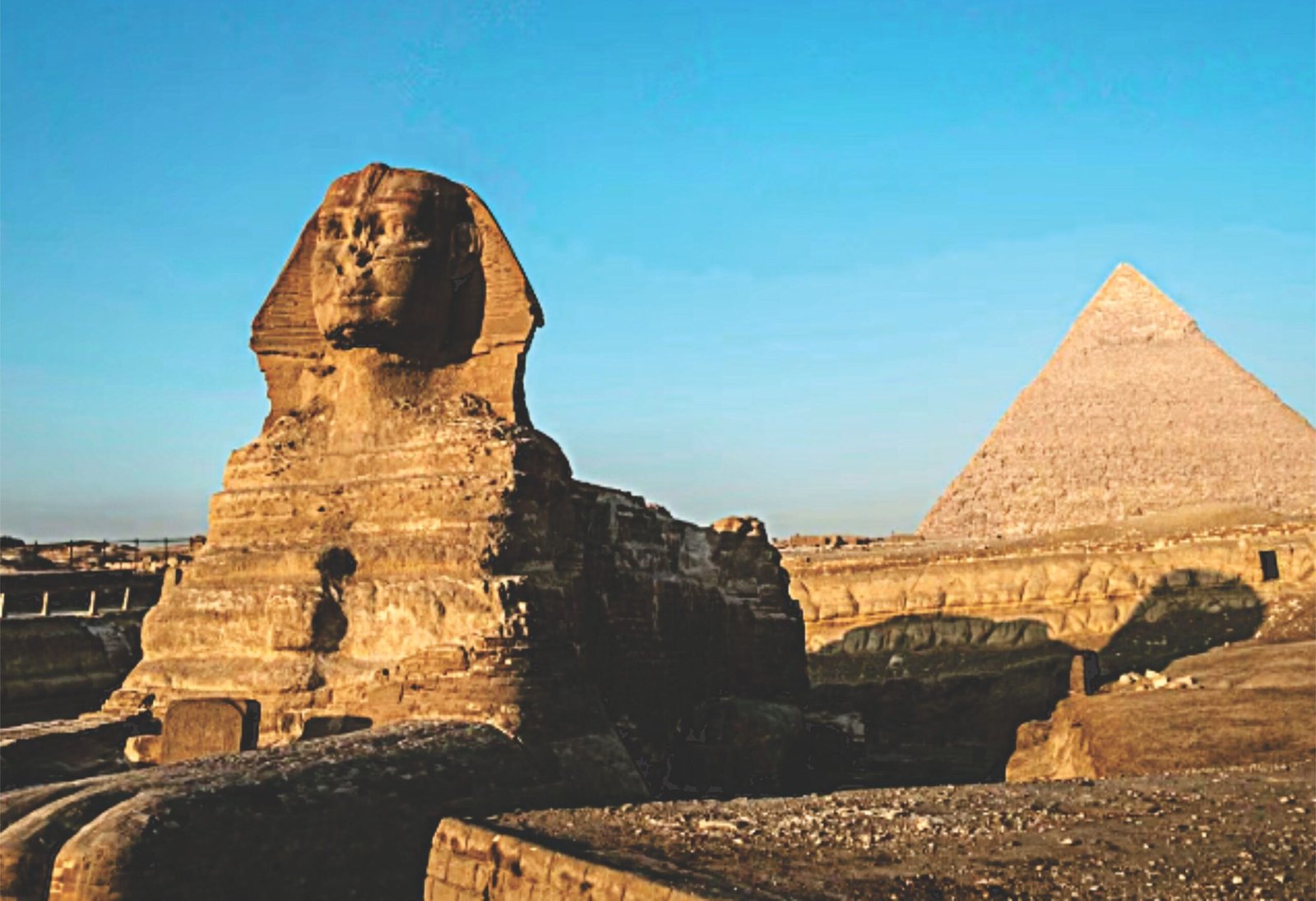
From Nubia to Egypt
Moving east, we find Somalia, which boasts a history of ancient trading civilizations such as the Puntites, known to the Egyptians as a land of wealth, resources, and exotic goods. The narratives of trade with ancient Egypt illustrate the interconnections between these civilizations, revealing a web of commerce and cultural exchange that underpins the history of the Horn of Africa.
Beyond Somalia, the great lakes region, which encompasses parts of modern Tanzania, offers insights into civilizations that thrived long before colonial influences reshaped the continent. The region that includes Tanganyika was home to various chiefdoms and societies that engaged in fishing, agriculture, and trade that spanned across East Africa. The integration of different cultures and influences helped shape the unique identity of these societies.

Thus, while Egypt stands as a pinnacle of ancient civilization in many discussions, it is essential to view it as part of a larger and vibrant picture of African history. From the monumental achievements of Aksum to the rich trade networks of Somalia and the societal structures in Uganda and Tanganyika, these ancient civilizations collectively forged a narrative that speaks to the diversity and complexity of human development on the African continent. Each played a crucial role in the advancement of culture, technology, and trade, creating a legacy that endures to this day, reminding us that the history of Africa is one rich with shared heritage and interconnectedness.
Kingdom of Nubia
The ancient kingdom of Nubia, located to the south of Egypt along the Nile River, is a significant yet often overlooked civilization in the annals of history. This region was known for its rich cultural and economic ties to neighboring Egypt and played a crucial role in shaping the history of northeastern Africa. While Egypt often garners more attention due to its monumental architecture and iconic figures, the kingdom of Nubia was equally influential during its height, showcasing a complex and dynamic culture that thrived long before Egypt’s renowned epochs.

Nubia, encompassing parts of modern-day Sudan and southern Egypt, is primarily divided into two historical regions: Upper Nubia and Lower Nubia. Upper Nubia, known for its mountainous terrain and rich mineral resources, primarily gold, served as a vital region that productively engaged in trade. Lower Nubia, on the other hand, was characterized by fertile lands and strategic trade routes, which fostered the growth of towns and cities.
Continue to Part III (God Hapi)